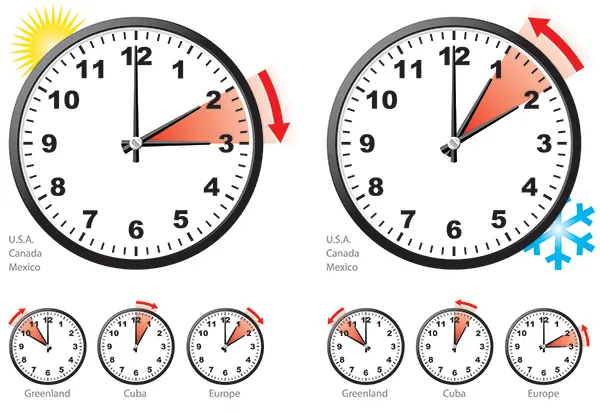
Daylight Saving Time is a system developed for maximizing daylight hours during the summer months.
In the Northern Hemisphere, clocks are normally set ahead one hour in March/April and set back one hour in September/October. Benjamin Franklin was the first to suggest the idea in an essay he wrote in 1784.
Originally the bill was rejected by the British House of Commons in 1909 but during World War I, multiple countries embraced the idea so they could conserve fuel by using less artificial light, including Australia, Great Britain, Germany, and the United States.
Throughout the years the start and end date of Daylight Savings has changed in different countries at different times but the principle objective, to enhance the normal daylight hours during summer remains the same.
Bibliography:
Encyclopædia Britannica. (n.d.). Daylight Saving Time . [image]. Britannica School. Retrieved November 8, 2023, from https://school.eb.com/levels/high/assembly/view/162057
Encyclopædia Britannica. (n.d.). Daylight Saving Time. Britannica School. Retrieved November 8, 2023, from https://school.eb.com/levels/high/article/Daylight-Saving-Time/29565